# Irony
A modified version of the Irony project ([https://irony.codeplex.com](https://irony.codeplex.com)) with .NET Core support.
[](https://dev.azure.com/sunnycoding/Irony/_build/latest?definitionId=4)
Irony is a .NET Language Implementation Kit written originally by Roman Ivantsov, you should be able to find his blog related to Irony via [http://irony-roman.blogspot.com/](http://irony-roman.blogspot.com/). He also developed an ORM framework, VITA, which can be found [here](http://vita.codeplex.com/ "here").
Based on the fact that the project on its official site hasn't been updated for a long time (last commit was on Dec 13th 2013) and cannot support .NET Core, I just made a copy of the project and made some modifications in order to support .NET Core. I still kept the MIT license and made the project to be licensed under Roman's name.
## Major Changes
- Fixed the compile issues found during .NET Core migration
- Changed `StringComparer.InvariantCulture(IgnoreCase)` to `StringComparer.CurrentCulture(IgnoreCase)`
- Changed `char.GetUnicodeCategory()` to `CharUnicodeInfo.GetUnicodeCategory(current)`
- Temporary removed `ParseTreeExtensions` implementation
- Migrated the unit test project to xUnit
- Removed the original `Test`, `Sample`, `GrammarExplorer` projects from the Visual Studio solution. And the GrammarExplorer is supposed to be provided in another repo
## Adding the NuGet Package
The Irony and Irony.Interpreter packages have been published to NuGet, with the package id `Irony.NetCore` and `Irony.Interpreter.NetCore`, in distinguishing from the original `Irony` and `Irony.Interpreter` packages published by Roman.
## Example
This repo contains a full example of an arithmetic expression evaluator, which accepts an arithmetic expression as a string and evaluates and calculates the result. You can find the source code under `Irony.SampleApp` folder. The expression grammar can be represented by the following C# class:
```cs
using Irony.Interpreter.Ast;
using Irony.Parsing;
using System;
namespace Irony.SampleApp
{
///
/// Represents the grammar of a custom expression.
///
///
[Language("Expression Grammar", "1.0", "abc")]
public class ExpressionGrammar : Grammar
{
///
/// Initializes a new instance of the class.
///
public ExpressionGrammar() : base(false)
{
var number = new NumberLiteral("Number");
number.DefaultIntTypes = new TypeCode[] { TypeCode.Int16, TypeCode.Int32, TypeCode.Int64 };
number.DefaultFloatType = TypeCode.Single;
var identifier = new IdentifierTerminal("Identifier");
var comma = ToTerm(",");
var BinOp = new NonTerminal("BinaryOperator", "operator");
var ParExpr = new NonTerminal("ParenthesisExpression");
var BinExpr = new NonTerminal("BinaryExpression", typeof(BinaryOperationNode));
var Expr = new NonTerminal("Expression");
var Term = new NonTerminal("Term");
var Program = new NonTerminal("Program", typeof(StatementListNode));
Expr.Rule = Term | ParExpr | BinExpr;
Term.Rule = number | identifier;
ParExpr.Rule = "(" + Expr + ")";
BinExpr.Rule = Expr + BinOp + Expr;
BinOp.Rule = ToTerm("+") | "-" | "*" | "/";
RegisterOperators(10, "+", "-");
RegisterOperators(20, "*", "/");
MarkPunctuation("(", ")");
RegisterBracePair("(", ")");
MarkTransient(Expr, Term, BinOp, ParExpr);
this.Root = Expr;
}
}
}
```
The following class diagram illustrates the object model that can represent an arithmetic expression, the classes shown in this diagram can be found under `Irony.SampleApp.Evaluations` namespace.
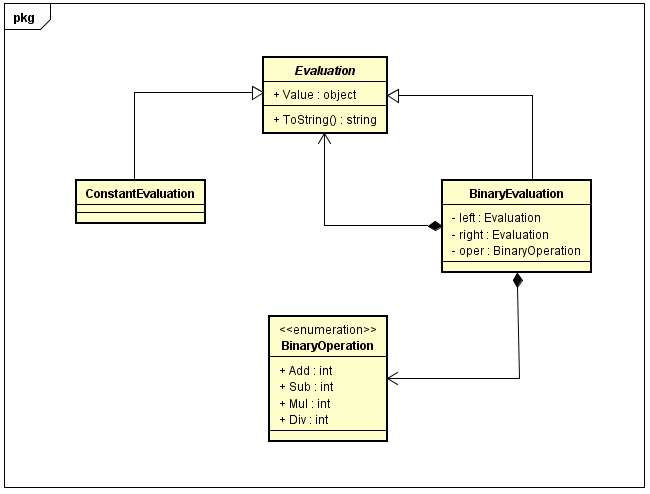
The `Evaluator` class under `Irony.SampleApp.Evaluations` namespace is responsible for creating the parser based on the above expression grammar definition and parse the input string and finally comes out the evaluated value.
```cs
using Irony.Parsing;
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace Irony.SampleApp.Evaluations
{
internal sealed class Evaluator
{
public Evaluation Evaluate(string input)
{
var language = new LanguageData(new ExpressionGrammar());
var parser = new Parser(language);
var syntaxTree = parser.Parse(input);
if (syntaxTree.HasErrors())
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(BuildParsingErrorMessage(syntaxTree.ParserMessages));
}
return PerformEvaluate(syntaxTree.Root);
}
private Evaluation PerformEvaluate(ParseTreeNode node)
{
switch (node.Term.Name)
{
case "BinaryExpression":
var leftNode = node.ChildNodes[0];
var opNode = node.ChildNodes[1];
var rightNode = node.ChildNodes[2];
Evaluation left = PerformEvaluate(leftNode);
Evaluation right = PerformEvaluate(rightNode);
BinaryOperation op = BinaryOperation.Add;
switch (opNode.Term.Name)
{
case "+":
op = BinaryOperation.Add;
break;
case "-":
op = BinaryOperation.Sub;
break;
case "*":
op = BinaryOperation.Mul;
break;
case "/":
op = BinaryOperation.Div;
break;
}
return new BinaryEvaluation(left, right, op);
case "Number":
var value = Convert.ToSingle(node.Token.Text);
return new ConstantEvaluation(value);
}
throw new InvalidOperationException($"Unrecognizable term {node.Term.Name}.");
}
private static string BuildParsingErrorMessage(LogMessageList messages)
{
var sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine("Parsing failed with the following errors:");
messages.ForEach(msg => sb.AppendLine($"\t{msg.Message}"));
return sb.ToString();
}
}
}
```
And the `Program.Main` method simply creates the evaluator and output the evaluated value:
```cs
using Irony.SampleApp.Evaluations;
using System;
namespace Irony.SampleApp
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var evaluator = new Evaluator();
var evaluation = evaluator.Evaluate("2.5+(3-1)*5");
Console.WriteLine(evaluation.Value);
}
}
}
```
Program output: